by Europeana (https://unsplash.com/@europeana)
In recent years, the connection between sleep apnea and cardiovascular health has gained significant attention. Sleep apnea, a condition characterized by frequent interruptions in breathing during sleep, not only affects sleep quality but also poses serious risks to heart health. Understanding this link is crucial for heart disease prevention and managing overall health. Let’s delve into the relationship between sleep apnea and heart disease and explore ways to manage this condition effectively.
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder where a person experiences repeated pauses in breathing during sleep. These interruptions can last from a few seconds to minutes and may occur multiple times per hour. There are two main types: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea. OSA, the more prevalent form, occurs when throat muscles intermittently relax and block the airway.
Sleep Apnea Symptoms
Recognizing sleep apnea symptoms is the first step in addressing the condition. Common symptoms include loud snoring, gasping for air during sleep, waking up with a dry mouth, morning headaches, and excessive daytime sleepiness. If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
How Sleep Apnea Affects Heart Health
by Europeana (https://unsplash.com/@europeana)
The link between sleep apnea and heart disease is well-documented. Here’s how sleep apnea can affect cardiovascular health:
Cardiovascular Complications of Sleep Apnea
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Frequent interruptions in breathing can lead to increased blood pressure levels. Obstructive sleep apnea and hypertension are closely related, as the body struggles to maintain oxygen levels, causing stress on the cardiovascular system.
- Heart Disease: Sleep apnea can contribute to the development of heart disease by causing inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. This can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition where arteries become narrowed and hardened due to plaque buildup.
- Heart Failure: Over time, untreated sleep apnea can lead to heart failure. The constant strain on the heart to pump blood effectively under conditions of low oxygen can weaken the heart muscles.
- Arrhythmias: Sleep apnea increases the risk of arrhythmias, or irregular heartbeats. These can lead to more severe conditions like stroke or sudden cardiac arrest.
Sleep Apnea Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing sleep apnea, including obesity, age, gender, and family history. Men, especially those overweight or over the age of 40, are at a higher risk. Lifestyle factors such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to the risk.
Managing Sleep Apnea for Heart Health
Managing sleep apnea effectively is essential for reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications. Here are some strategies:
Lifestyle Changes
- Weight Management: Losing weight can significantly reduce the severity of sleep apnea in overweight individuals. Even a modest weight loss can have a positive impact on symptoms.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet low in saturated fats and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can improve overall cardiovascular health.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce sleep apnea severity.
- Avoid Alcohol and Smoking: Reducing alcohol intake and quitting smoking can improve sleep quality and decrease the risk of sleep apnea.
Sleep Apnea Treatment Benefits

by Kristin Snippe (https://unsplash.com/@frausnippe)
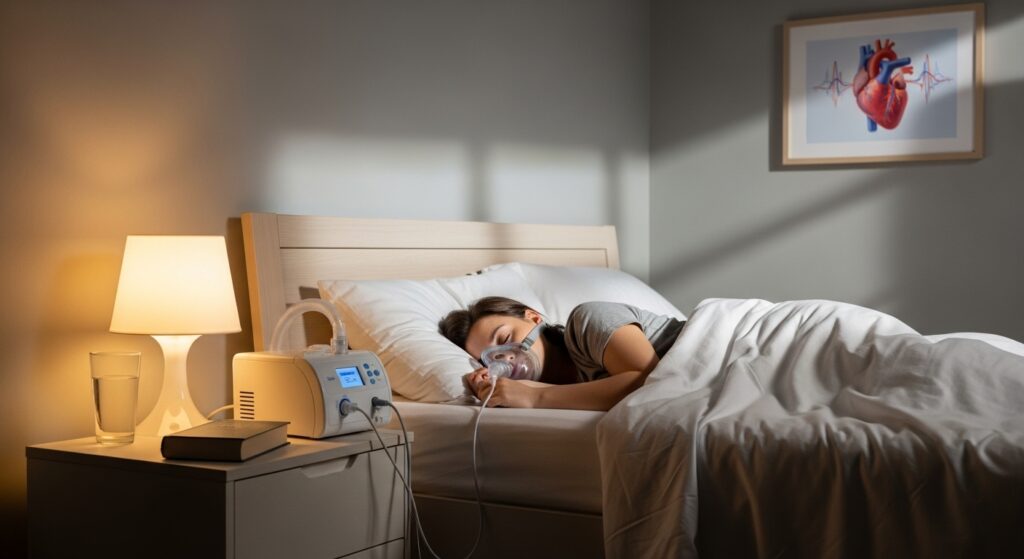
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): CPAP therapy is the most common and effective treatment for obstructive sleep apnea. It involves wearing a mask over the nose and/or mouth during sleep, which provides a constant stream of air to keep the airways open.
- Oral Appliances: Dental devices that reposition the lower jaw and tongue can be an option for mild to moderate sleep apnea cases.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical options such as removing excess tissue from the throat or realigning the jaw may be considered.
- Positional Therapy: Some individuals experience sleep apnea primarily when sleeping on their back. Positional therapy encourages sleeping on the side to reduce symptoms.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea are crucial for preventing cardiovascular complications. If you suspect you have sleep apnea, seek medical advice promptly. A sleep study, often conducted in a sleep clinic or at home with portable monitors, can help diagnose the condition.
Conclusion
Understanding the link between sleep apnea and cardiovascular health is essential for heart disease prevention. By recognizing the symptoms, understanding the risks, and managing the condition effectively through lifestyle changes and treatment, you can protect your heart and improve your overall quality of life. If you or a loved one experiences symptoms of sleep apnea, consult a healthcare provider to explore the best management options for your needs.
By taking proactive steps to manage sleep apnea, you can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications and lead a healthier, more restful life.





